The Steam Header simulates a steam header by distributing steam to the outlets to meet steam demands.
The Steam Header is normally used with one or two control streams which are attached to steam supply streams. The Steam Header adjusts the flow in the steam supply streams to balance the flow around the header.
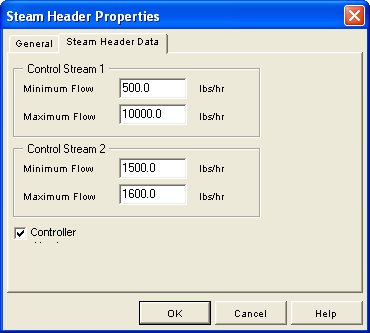
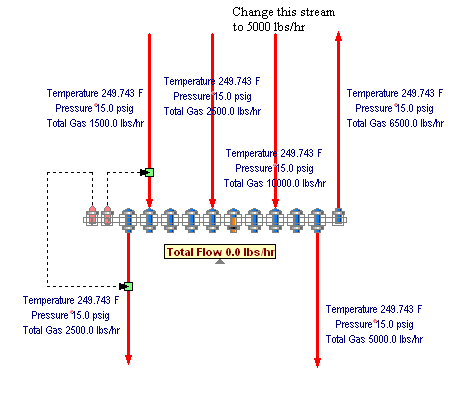
Control streams and their attach steam supply are adjusted in order. Control stream 1 is increased first and decreased the ast.
While not required, the Sky Steam stream should exist. The Steam Header uses the Sky Steam stream during intermediate iterations and for the case when the steam supply exceeds the steam demand.
What do you want to see?
 Data
Description Data
Description |
 Equipment
Properties Equipment
Properties |
 Example Example |
 Method&Equations Method&Equations |
 Warnings Warnings |
 Errors Errors |

 Warnings
Warnings 
 Errors
Errors